Covariance Matrix of Multivariate Gaussian Distributions: A Detailed Exploration
Covariance: The Foundation
Covariance measures how much two random variables change together. It is defined for two variables $X$ and $Y$ as:
\[\text{Cov}(X, Y) = \mathbb{E}[(X - \mathbb{E}[X])(Y - \mathbb{E}[Y])]\]This measure is positive if the variables tend to move in the same direction, negative if they move in opposite directions, and zero if there is no linear relationship.
The Covariance Matrix
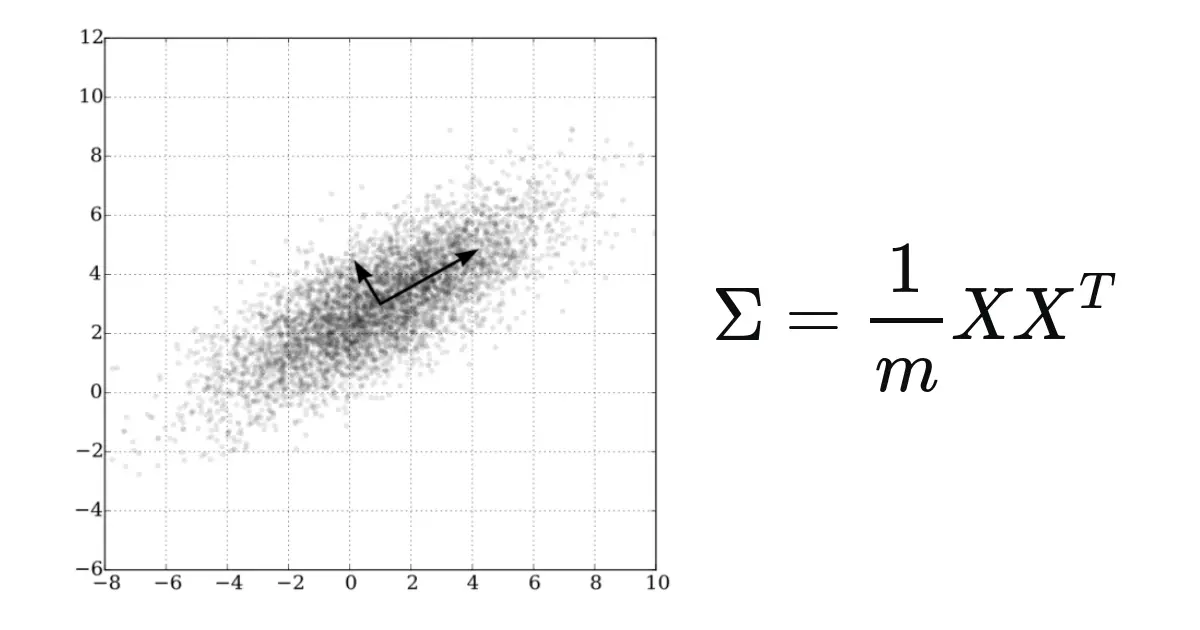
For a random vector $\mathbf{X} = (X_1, X_2, \dots, X_n)$, the covariance matrix $\Sigma$ encapsulates the covariance between every pair of components. It is defined as:
\[\Sigma = \mathbb{E}[(\mathbf{X} - \mathbb{E}[\mathbf{X}])(\mathbf{X} - \mathbb{E}[\mathbf{X}])^T]\]Expanding this definition, the covariance matrix can be represented in matrix form as:
\[\Sigma = \begin{bmatrix} \sigma_{11} & \sigma_{12} & \cdots & \sigma_{1n} \\ \sigma_{21} & \sigma_{22} & \cdots & \sigma_{2n} \\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ \sigma_{n1} & \sigma_{n2} & \cdots & \sigma_{nn} \end{bmatrix}\]where $\sigma_{ij} = \text{Cov}(X_i, X_j)$.
Covariance Matrix in Multivariate Gaussian Distributions
In multivariate Gaussian distributions, the covariance matrix not only describes variance and covariance but also completely characterizes the distribution. A multivariate Gaussian distribution is defined by:
\[\mathbf{X} \sim N(\mu, \Sigma)\]where $\mu$ is the mean vector and $\Sigma$ is the covariance matrix.
Special Properties
- Diagonal Covariance Matrix: If $\Sigma$ is diagonal, the variables are uncorrelated, and each variable $X_i$ varies independently of the others.
- Identity Matrix: If $\Sigma$ is the identity matrix, the variables are uncorrelated and all have unit variance.
- Zero Off-Diagonal Elements: For multivariate Gaussian distributions, zero off-diagonal elements (indicating zero covariance) imply that the variables are independent. This is a unique property of Gaussian distributions, where uncorrelatedness implies independence.
Importance in Statistical Analysis
The covariance matrix is crucial in many statistical techniques, such as principal component analysis (PCA) for dimensionality reduction, and in various predictive modeling methods. Understanding the covariance matrix helps in assessing the underlying structure of the data, evaluating relationships among variables, and making informed decisions about the appropriate models to use.
Conclusion
The covariance matrix is a fundamental concept in the analysis of multivariate Gaussian distributions, providing deep insights into the relationships between variables. Its comprehensive representation of variance and covariance makes it an indispensable tool in multivariate statistical analysis, helping to illuminate the complex interdependencies in multivariate data. This understanding is crucial for effectively modeling and interpreting multivariate phenomena in various scientific and practical fields.